Accounting Practice Management Software emerged in the 1990s and become popular in the early 2000s as a specialized solution to help accounting firms streamline their operations. Traditionally, accountants relied on general project management tools, spreadsheets, and email for task tracking, client communications, and document management. However, as firms grew, the need for dedicated tools tailored to the nuances of accounting workflows became evident.
This category addresses challenges like tracking billable hours, managing recurring client tasks (e.g., tax filings or audits), and centralizing client documents securely. By integrating accounting-specific workflows with tools for collaboration, billing, and compliance, this software enables accountants to manage their practices more efficiently while maintaining regulatory standards.

Software specifically built for accounts payable focuses exclusively on automating and optimizing AP processes, offering advanced features like fraud detection, compliance management, and customizable workflows tailored to payment and vendor management. In contrast, general accounting software includes accounts payable as one of many functions, providing basic AP capabilities but often lacking the specialized tools and efficiency of dedicated AP solutions.
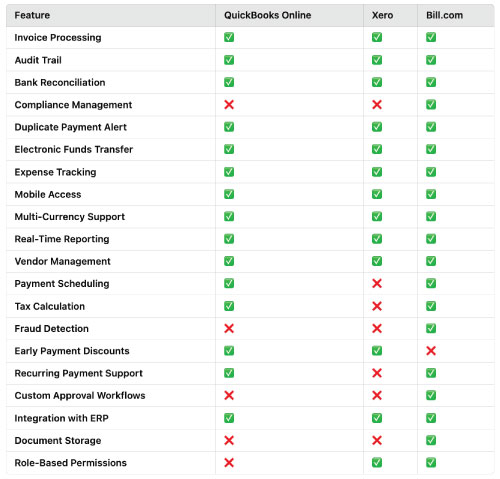
When assessing different accounts payable solutions to determine which one works for your needs, it’s helpful to make a comparison chart like the example below, which compares 20 of the most pertinent features of accounts payable software with several of the most popular software providers in that category.
This video from the Business Solution YouTube channel takes a look at the different approaches to using accounts payable software, including reviewing some of the most popular tools in the category: Bill.com, Melio, Sage 100, Quadient, and QuickBooks Online Plus.
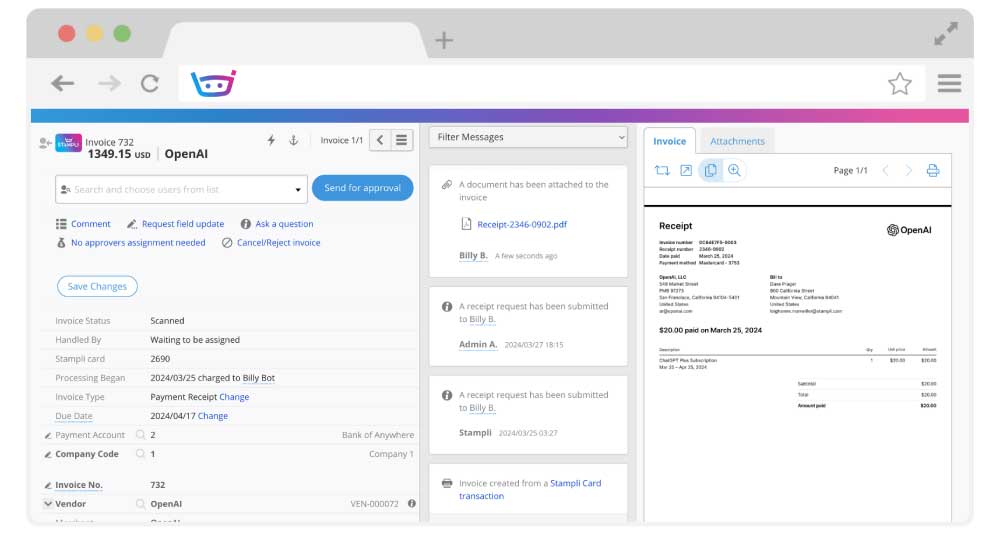
The screenshot above from Stampli demonstrates some of the core functionality of accounts payable software, including matching up invoices with payment receipts, tracking vendors, incorporating user permissions, and other aspects of accounts payable software.
When you’re choosing an appropriate accounts payable software solution, here are some pertinent features to keep in mind. This is a fairly comprehensive list of product features available from various accounts payable software solutions. Some of these may not be applicable to your organization or to your specific scenario. Before shopping for accounts payable software, it’s best to determine based upon your operational habits which features are critical, which might be nice to have, and which could be distractions that make the software more difficult to use.