Application development software enables developers to design, build, test, and deploy applications across platforms such as web, mobile, and desktop. Over time, these tools have evolved from basic programming editors to robust platforms integrating features like debugging, cloud deployment, and automated testing.
Examples of leading software in this category include Visual Studio, Xcode, Android Studio, OutSystems, and Flutter. Related categories include Low-Code Development Platforms, DevOps Tools, and Software Testing Tools, which often complement application development software to support the end-to-end development lifecycle.

The table below compares the most essential features of three leading application development tools. Use this table to evaluate which tool best fits your specific project requirements.
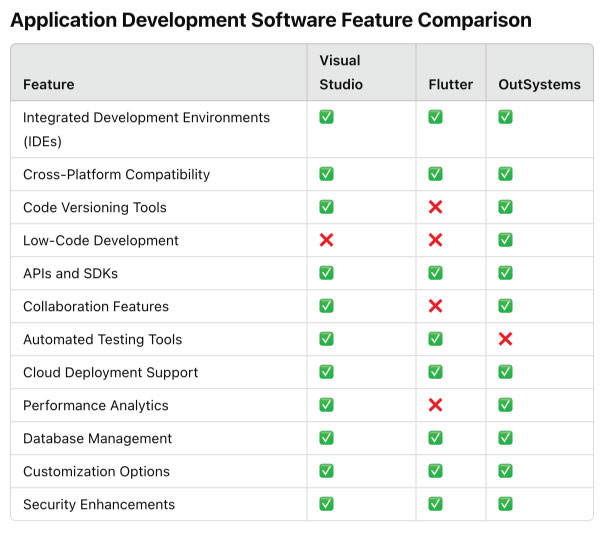
The feature comparison chart highlights the strengths and specializations of each tool within the application development software category. Visual Studio stands out as the most comprehensive option, offering robust support for IDEs, collaboration features, automated testing, and performance analytics. Flutter excels in cross-platform compatibility and lightweight development but lacks advanced collaboration and testing tools. OutSystems, as a low-code platform, shines in its ease of use and rapid application deployment, though it falls short in automated testing and detailed performance monitoring. This variation in feature sets underscores the importance of selecting a tool based on project-specific needs, whether prioritizing advanced coding capabilities, ease of use, or platform versatility.
This evaluation suggests that Greenhouse suits larger organizations with diverse needs, Workable is ideal for user-friendly, AI-driven recruitment, and BambooHR excels for businesses seeking integration with broader HR functions.
This video offers an insightful look into the key aspects of an application development system, exploring the tools, processes, and methodologies that streamline app creation. Whether you’re a developer, product manager, or just curious about how modern apps are built, this video breaks down the complexities of development environments, collaboration tools, and deployment workflows in an accessible way. Watch to understand how systems like IDEs, APIs, and cloud platforms come together to bring applications from concept to reality.
This dashboard example represents a typical interface used in application development software, showcasing the tools and features that developers rely on to build, manage, and optimize applications. The central workspace includes a live code editor for real-time programming, surrounded by essential panels such as a project timeline with milestones, task management for tracking team progress, and performance metrics to monitor system resource usage and error rates. A side menu provides quick access to key functions like deployment tools, version control systems, and collaboration features. This design highlights how these systems streamline the development workflow, improve productivity, and ensure high-quality app delivery.
Application development software includes a range of features to simplify and accelerate the development process. Whether you’re coding complex software from scratch or building apps using drag-and-drop interfaces, these tools are designed to meet a variety of needs. Below, we’ll dive deeper into the most important features, showcasing how they support developers in creating high-quality applications efficiently.
Application development software helps developers build, test, and deploy apps across multiple platforms efficiently.
Low-code platforms accelerate development by reducing the need for manual coding, making app creation accessible to non-developers.
An IDE is a tool for writing and debugging code, while a framework provides pre-built libraries and components for application development.
Cross-platform tools are great for general apps but may not provide the same level of performance optimization as platform-specific development.
Tools like OutSystems and Flutter are beginner-friendly due to their low-code options and intuitive design.
AI has transformed application development by introducing features such as intelligent code suggestions, automated debugging, and predictive analytics. Tools like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine now assist developers by generating code snippets, reducing errors, and accelerating workflows. Additionally, AI enables the automation of testing processes, performance optimization, and even low-code/no-code solutions, allowing non-technical users to create functional apps.
Microservices architecture allows applications to be built as a collection of loosely coupled services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Application development software increasingly supports this architecture by offering features like API integration, containerization tools (e.g., Docker), and orchestration platforms (e.g., Kubernetes). This approach enhances scalability, flexibility, and resilience in large, complex applications.
Modern application development tools incorporate features like secure coding standards, vulnerability scanning, and real-time threat detection. Tools such as Snyk and SonarQube help identify and fix security flaws in code, while integrations with authentication libraries and encryption tools ensure secure data handling. Security-focused frameworks and plugins further reinforce application integrity.
CI/CD pipelines automate the integration and deployment of code changes, enabling faster and more reliable updates. Application development software like Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, and Azure DevOps provides built-in support for pipelines, allowing developers to automate tasks such as testing, building, and deploying applications. This reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and ensures faster delivery cycles.
Containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes have revolutionized how applications are developed, tested, and deployed. Application development software now integrates with these technologies, allowing developers to create consistent environments across development, testing, and production. This ensures applications behave predictably, regardless of the underlying infrastructure, while improving scalability and resource management.