Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Software encompasses tools that help manage the entire software development lifecycle, from ideation and requirements gathering to deployment, maintenance, and decommissioning. ALM ensures that all stakeholders, including developers, project managers, and QA teams, collaborate effectively.
Popular ALM tools like Jira Software, Microsoft Azure DevOps, and Micro Focus ALM have shaped the category by offering robust features for requirements management, defect tracking, and continuous integration. Related software categories include DevOps tools, project management software, and software testing tools, which complement ALM by addressing specific lifecycle stages.
The table below compares features across three popular ALM tools, helping organizations choose software that best aligns with their needs. Each feature is evaluated based on its presence and implementation in these tools.
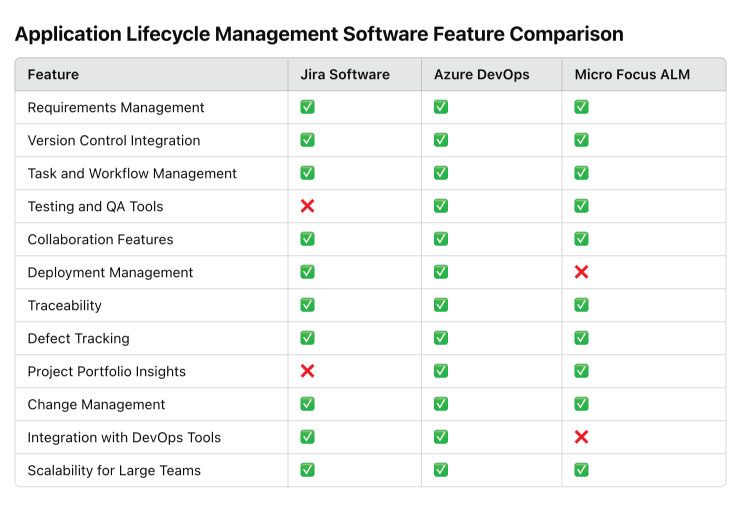
The feature comparison table highlights the strengths and variations among Jira Software, Azure DevOps, and Micro Focus ALM. All three tools excel in requirements management, version control integration, and defect tracking, making them strong contenders for comprehensive ALM solutions.
However, Azure DevOps stands out for its extensive support for testing and deployment management, making it an excellent choice for teams heavily focused on CI/CD processes. Meanwhile, Micro Focus ALM is a clear leader in traceability and project portfolio insights, catering to enterprise-scale and compliance-driven projects.
Notably, Jira Software is an agile-focused tool that excels in collaboration and task management, but lacks integrated testing tools, requiring users to complement it with third-party solutions. This variation in capabilities shows how ALM tools can align with specific team needs, whether agile development, enterprise governance, or DevOps pipelines.
To further explore the value and functionality of Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Software, this video provides a concise and insightful overview of what ALM is, why it matters, and how it supports teams throughout the software development lifecycle. Covering key concepts such as requirements management, collaboration, and deployment workflows, the video offers practical examples and explains how ALM tools streamline processes, improve quality, and enhance team productivity.
This resource is especially helpful for those new to ALM or looking to understand how tools like Jira Software, Azure DevOps, or Micro Focus ALM can transform their development processes. Watch the video to gain a foundational understanding of how ALM software ties together every phase of software development into a cohesive, efficient framework.
This image illustrates a sample dashboard for Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) software, showcasing the core features and functionality that support the entire software development lifecycle. The dashboard integrates key tools, including:
The clean, modern design and professional color scheme emphasize functionality and usability, reflecting the powerful, all-in-one nature of ALM software. This image provides a snapshot of how ALM tools bring together diverse features to help teams collaborate, stay organized, and deliver high-quality software.
ALM software is defined by its comprehensive suite of tools that span the entire software lifecycle. Each feature contributes to improving efficiency, reducing errors, and fostering collaboration across teams. Below, we provide a detailed look at the key capabilities that define this software category.
ALM software ensures that every stage of software development is effectively planned, executed, and monitored, improving collaboration and quality.
While ALM covers the entire lifecycle, DevOps tools focus on automating deployment, testing, and infrastructure management within that lifecycle.
Yes, many ALM tools, such as Jira Software, are tailored to agile methodologies with features like sprint planning and backlog management.
Industries like IT, healthcare, finance, and automotive benefit greatly from ALM software due to complex projects and compliance needs.
Yes, while enterprise-focused, many ALM tools offer scalable solutions and pricing tiers that fit small team needs.
ALM software uses centralized repositories to store all project artifacts—such as requirements, tasks, test cases, and source code—while maintaining a connected history of changes. Traceability matrices link these artifacts to ensure every requirement is fulfilled and every change is accounted for, supporting compliance, quality assurance, and root-cause analysis.
Yes, many ALM tools, such as Azure DevOps and GitLab, natively integrate with containerization platforms like Docker and Kubernetes. These integrations streamline deployment workflows by automating container builds, orchestration, and scaling, enabling developers to deliver software faster and more efficiently.
ALM tools provide configurable workflows to support diverse methodologies. For example, agile teams can use sprint-based task boards and backlog management, while waterfall projects can leverage linear project timelines and milestone tracking. Many tools, like Jira and Polarion, also allow hybrid approaches for teams transitioning between methodologies.
AI in ALM software enhances productivity and decision-making by automating repetitive tasks, predicting project risks, and providing insights. For example, AI can analyze historical data to identify potential bottlenecks, prioritize bug fixes based on impact, or suggest optimal resource allocation. AI-driven testing tools can also automate the generation and execution of test cases, further improving efficiency.
ALM tools integrate with popular version control systems (e.g., Git, SVN, Mercurial) to manage code repositories for multi-team environments. They support branching, merging, and conflict resolution workflows while tracking changes across teams. Advanced features like permissions management and audit logs ensure collaboration without sacrificing security or traceability.