Architectural CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software revolutionizes the way architects, engineers, and designers conceptualize and develop building projects. These tools enable precise drafting, 3D modeling, and documentation, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy in architectural workflows. Over time, CAD software has evolved to incorporate Building Information Modeling (BIM), real-time collaboration, and advanced rendering features, making it indispensable for modern architecture firms. Notable software in this category includes AutoCAD Architecture, Revit, ArchiCAD, Vectorworks Architect, and SketchUp. Related software categories include Structural Engineering Software, Interior Design Software, and Landscape Design Software.

The table below provides a comparison of key features across three leading Architectural CAD software options. This overview helps users understand feature availability and make informed purchasing decisions.
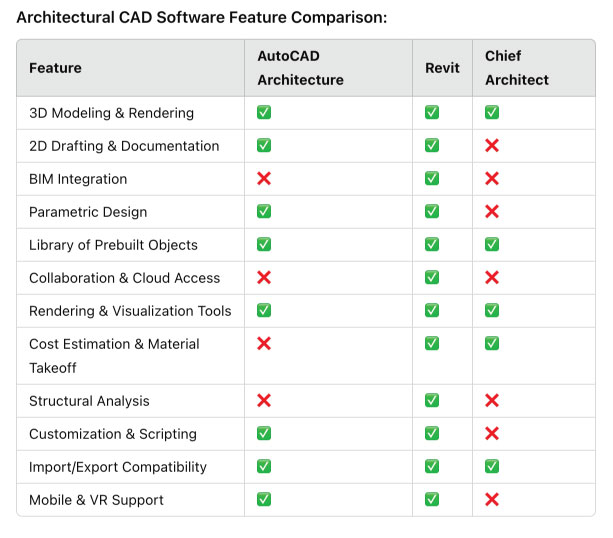
The feature comparison table highlights key differences between the software options. While Revit stands out for its comprehensive support of BIM integration and structural analysis, AutoCAD Architecture is better suited for detailed 2D drafting. Meanwhile, Chief Architect caters to residential projects with a focus on prebuilt object libraries but lacks advanced features like BIM or parametric design. This diversity allows users to select the tool that best aligns with their specific needs.
For those looking to gain a deeper understanding of Architectural CAD software, this video provides a comprehensive overview of essential features and real-world applications. It explores key functions such as 3D modeling, parametric design, and BIM integration, demonstrating how professionals use these tools to streamline architectural workflows. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced designer, this resource will help you see how CAD software enhances precision, collaboration, and visualization in architectural projects. Watch to learn more about how these tools transform the way buildings are designed and developed!
This image represents a typical architectural CAD software dashboard, showcasing essential tools and features used by architects and designers. The interface includes a detailed 3D building model, an interactive 2D floor plan, and a comprehensive set of design tools for drafting, modeling, and rendering. A side panel displays a materials library and object properties, while a lower toolbar provides quick access to commonly used functions such as measurements, layers, and object manipulation. The modern color scheme, with dark gray and blue highlights, reflects the precision and technical nature of CAD software, making it an essential tool for architectural visualization and construction planning.
Architectural CAD software provides a robust suite of tools that streamline the design and documentation process. From detailed 2D drafting to immersive 3D visualization, these programs support architects in creating highly accurate and efficient designs. Essential features include parametric modeling, BIM integration, and real-time collaboration, ensuring seamless workflows from conceptual design to construction documentation. Below, we explore these features in greater detail.
CAD focuses on drafting and modeling, while BIM incorporates data-rich 3D models for comprehensive building planning.
Some programs, like SketchUp, are beginner-friendly, while others, like Revit, have a steeper learning curve.
Yes, many programs like ArchiCAD and Vectorworks Architect support macOS, but some, like Revit, require virtualization.
Yes, many tools offer cloud collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on a project simultaneously.
Requirements vary, but most software needs a high-performance processor, dedicated GPU, and ample RAM (16GB+ recommended).
Most CAD software supports DWG, DXF, IFC, RVT, SKP, and STL formats, ensuring compatibility with other design tools.
They use optimizations like level-of-detail rendering, linked files, cloud processing, and efficient memory management to handle large models.
A dedicated GPU accelerates rendering, real-time visualization, and complex geometric computations, significantly improving performance.
Yes, many support scripting languages like Python, Lisp, or Dynamo, allowing automation and custom tool creation.
Many platforms use cloud-based file versioning, automatic save points, and model history tracking to manage changes effectively.