Architecture software provides architects, designers, and engineers with powerful tools to create, plan, and document their projects. These applications range from traditional CAD (Computer-Aided Design) programs to advanced BIM (Building Information Modeling) platforms that integrate data-driven design. Software like AutoCAD Architecture, Revit, SketchUp, Archicad, and Vectorworks Architect are widely used in the industry for various design needs.
This category of software enables users to create highly detailed 2D and 3D architectural drawings, streamline collaboration, and integrate with construction management tools. Related software categories include Interior Design Software, Structural Engineering Software, and Construction Management Software.

The feature comparison table below highlights how different architecture software solutions implement key capabilities. It helps users choose the right software based on their specific needs, whether it’s advanced BIM functionality, real-time rendering, or cloud-based collaboration.
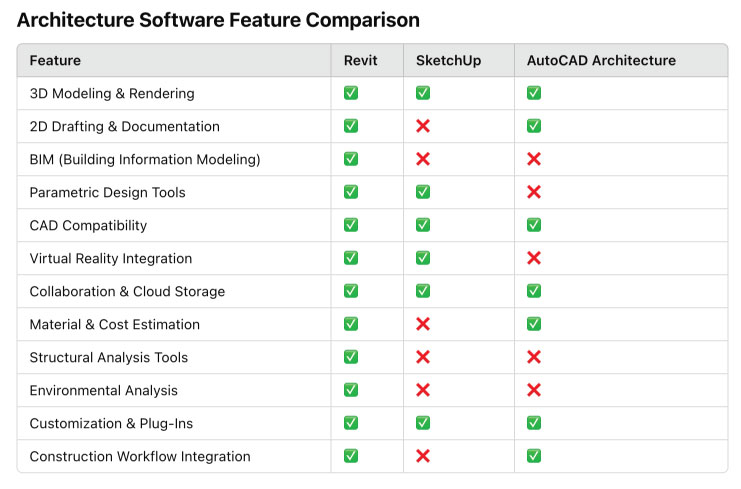
The feature comparison table highlights distinct strengths among Revit, SketchUp, and AutoCAD Architecture, with each excelling in different aspects of architectural design. Revit is the most comprehensive, offering advanced BIM capabilities, parametric design, and collaboration tools, making it ideal for large-scale, data-driven projects. However, its complexity and system requirements can be a drawback. SketchUp is highly intuitive and excels in 3D modeling and visualization, making it great for conceptual design, though it lacks BIM and advanced structural analysis. AutoCAD Architecture remains a top choice for precise 2D drafting and CAD workflows, but it lacks the modern visualization and collaboration features found in other tools. Ultimately, the best choice depends on whether the priority is BIM and project management, design flexibility, or technical drafting precision.
This video showcases some of the core functionalities of architecture software, demonstrating how modern tools enable architects to visualize, design, and document their projects with precision and efficiency. From 3D modeling and rendering to parametric design and BIM integration, the video highlights how software like Revit, SketchUp, and Rhino streamline the architectural workflow. You’ll see key features such as real-time collaboration, material estimation, and environmental analysis, which are essential for creating innovative and sustainable designs. Whether you’re an architect, designer, or student, this video provides a glimpse into how architecture software transforms ideas into detailed, buildable structures.
This dashboard represents a modern architecture software interface designed to streamline the design, planning, and management of architectural projects. Unlike traditional CAD software, which focuses on drafting and technical drawings, this dashboard integrates high-level project insights, real-time collaboration, and data-driven decision-making.
At its core, the dashboard features a 3D model preview of a futuristic building, allowing architects to interact with and refine their designs. The inclusion of BIM (Building Information Modeling) data panels enables precise material tracking, structural analysis, and lifecycle planning. Additionally, sustainability analysis graphs help evaluate a building’s environmental impact, optimizing energy efficiency and material choices.

Modern architecture software provides a blend of precision, efficiency, and creativity. From concept development to final documentation, these tools support architectural workflows with advanced modeling, drafting, and collaboration capabilities. Features like BIM integration, parametric design, and real-time rendering enhance productivity while cloud-based collaboration and sustainability analysis help architects design smarter and greener buildings.
Architecture software is a broad category that includes all digital tools used in architectural design, modeling, and planning, encompassing BIM (Building Information Modeling), parametric design, rendering, and environmental analysis. Architectural CAD software, on the other hand, is a subset of architecture software focused specifically on computer-aided drafting (CAD) for creating precise 2D and 3D drawings. While architectural CAD software like AutoCAD Architecture is primarily for drafting and documentation, architecture software like Revit, Archicad, and SketchUp offers a more comprehensive range of tools, including BIM and 3D visualization.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) in architecture software integrates intelligent, data-rich 3D models, allowing for real-time collaboration, material estimation, and lifecycle management. Unlike traditional CAD, which focuses on line-based 2D and 3D drafting, BIM software like Revit and Archicad stores detailed metadata about building components, making it ideal for planning, analysis, and construction management.
Parametric design enables architects to create rule-based, algorithmic models where changes to one parameter automatically update the entire design. Tools like Grasshopper (for Rhino) and Dynamo (for Revit) allow architects to generate complex, adaptive structures based on predefined logic, making it especially useful for generative design, facade optimization, and structural analysis.
Advanced architecture software, particularly BIM platforms like Revit, offers multi-disciplinary collaboration, allowing architects, structural engineers, and MEP designers to work within a shared model. These integrations help in clash detection, load calculations, and ensuring compliance with building codes, streamlining the entire design-to-construction workflow.
Architects use rendering engines to create high-quality visualizations for presentations and client approvals. Popular rendering engines integrated with architecture software include:
V-Ray (compatible with SketchUp, Revit, Rhino, and 3ds Max)
Enscape (real-time rendering for Revit, SketchUp, and Archicad)
Lumion (fast, photorealistic visualization)
Twinmotion (powered by Unreal Engine, offering real-time interactive walkthroughs)
Modern architecture software includes energy simulation and environmental analysis tools to optimize designs for sustainability. Revit and Archicad integrate solar exposure analysis, daylight studies, and thermal modeling, while plugins like Insight (for Revit) and Sefaira (for SketchUp) offer advanced energy performance simulations to improve building efficiency.
GIS integration allows architects to incorporate real-world geographical data into their designs, improving site analysis, urban planning, and environmental impact assessments. Software like ArcGIS can be integrated with Revit and Rhino to analyze topography, zoning regulations, and climate conditions, ensuring buildings are designed within the context of their environment.
Interoperability is essential for seamless collaboration between different software platforms. Common workflows include:
IFC (Industry Foundation Classes): An open BIM format that allows interoperability between Revit, Archicad, Vectorworks, and Tekla.
DWG/DXF: Standard CAD file formats for compatibility with AutoCAD-based applications.
3DM (Rhino): Used for transferring complex parametric and freeform geometry to Revit and Grasshopper.
OBJ/FBX: Used for 3D model exchange between SketchUp, Lumion, Twinmotion, and Blender for rendering and visualization.
AI and machine learning are transforming architecture software by enabling automated design generation, performance optimization, and predictive analytics. Examples include:
Generative design tools in Revit and Grasshopper, which suggest optimized spatial layouts based on constraints.
AI-driven clash detection in BIM 360, which predicts and resolves design conflicts before construction.
Machine learning-powered rendering enhancements in tools like V-Ray and Twinmotion, which improve photorealism and lighting accuracy.
Cloud computing allows architects to store, share, and process complex models in real time, improving collaboration and efficiency. Key benefits include:
Cloud-based BIM collaboration via Autodesk BIM 360 and Graphisoft BIMcloud.
Remote access to high-performance computing (HPC) for rendering and simulation.
Version control and model history tracking, preventing data loss and ensuring seamless project management.