Archiving software is designed to efficiently store, manage, and retrieve large volumes of data while ensuring compliance with legal and organizational policies. These solutions help businesses handle data lifecycle management, secure long-term storage, and optimize space usage through compression and deduplication.
Historically, archiving systems were limited to physical storage methods such as tape drives and optical disks. Modern archiving solutions now leverage cloud-based infrastructures, AI-driven indexing, and automated retention policies to enhance accessibility and security. Popular examples of archiving software include Veritas Enterprise Vault, Commvault, IBM Spectrum Archive, Microsoft Azure Archive Storage, and ZL Tech Unified Archive.
Related categories include Backup Software, Document Management Systems, Enterprise Content Management (ECM) Software, and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software.

Veritas Enterprise Vault – A leading archiving solution that automates email and file archiving while ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
Commvault – Provides comprehensive data management, including archiving, backup, and disaster recovery, with AI-powered search features.
IBM Spectrum Archive – Uses LTFS (Linear Tape File System) to enable long-term storage of large datasets with high reliability.
Microsoft Azure Archive Storage – A cloud-based archiving service offering scalable and cost-effective data retention solutions.
ZL Tech Unified Archive – Specializes in enterprise-level archiving with AI-driven analytics for compliance and governance.
GFI Archiver – A user-friendly archiving solution focused on email and document retention for SMBs.
Mimecast Cloud Archive – A cloud-based email archiving platform with advanced search, compliance, and e-discovery features.
Barracuda Message Archiver – A cloud-integrated email archiving solution designed for compliance, e-discovery, and storage optimization, with advanced search and retrieval capabilities.
Arcserve UDP Archiving – Provides email and file archiving with a focus on compliance and legal discovery, offering on-premises and cloud deployment options.
OpenText InfoArchive – A scalable, enterprise-grade solution that enables organizations to securely store and manage structured and unstructured data while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Google Vault – A cloud-based archiving and e-discovery tool for Google Workspace users, allowing organizations to retain, search, and export emails, chats, and files for compliance and legal purposes.
MailStore Server – A popular email archiving software designed for small and medium-sized businesses, offering efficient storage management, compliance support, and easy search functionality.
The following table compares three leading archiving software solutions based on their essential features. This comparison highlights differences in capabilities, helping businesses select the best solution for their needs.
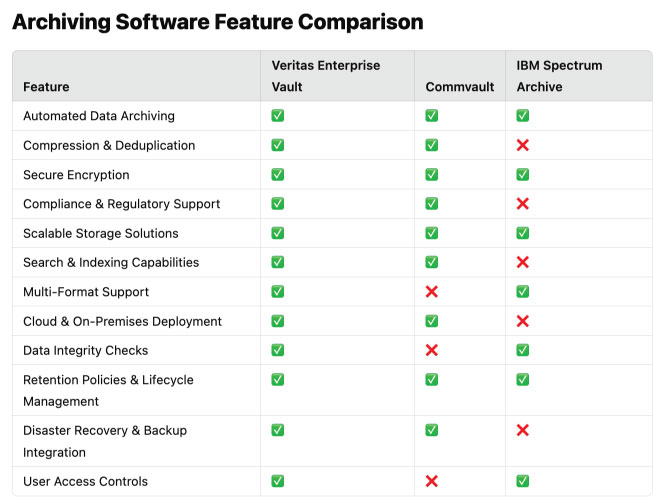
The feature comparison chart highlights the strengths and trade-offs of three leading archiving software solutions. Veritas Enterprise Vault stands out as the most comprehensive option, supporting all key features except for disaster recovery integration. It excels in compliance, security, and search capabilities, making it a strong choice for enterprises needing robust regulatory support and long-term data management. Commvault, while also highly capable, lacks multi-format support, data integrity checks, and user access controls, which may impact organizations that require strict security and flexible file handling. However, its strengths in disaster recovery, cloud deployment, and compression make it a solid choice for businesses prioritizing scalable and efficient data storage.
On the other hand, IBM Spectrum Archive focuses heavily on scalable storage and basic archiving functionality but lacks key enterprise-level features such as search and indexing, compliance support, and cloud deployment. This makes it more suitable for organizations that prioritize large-scale data storage over regulatory or security concerns. While it supports multi-format data and ensures data integrity, its limitations in disaster recovery and search functionality may present challenges for businesses needing quick data retrieval and compliance readiness. Overall, the comparison underscores that while some solutions provide all-around functionality, others trade certain features for specialization in specific areas like scalability or disaster recovery.
The following video delves into effective strategies for managing and storing data through archiving. It emphasizes the importance of freeing up primary cloud storage by transferring infrequently accessed data to archive storage solutions. The presentation covers key principles such as identifying data suitable for archiving, implementing efficient archiving processes, and ensuring that archived data remains accessible and secure. By following these best practices, organizations can optimize their storage resources, enhance data management efficiency, and maintain the integrity and availability of critical information.
This dashboard graphic represents a user interface for archiving software, showcasing key functionalities for managing archived data efficiently. The layout includes a storage usage chart, providing a visual overview of used and available space. A recent archived files list allows users to quickly access newly stored documents, while a search bar enables fast retrieval of specific files. Additional sections display the encryption status, compliance reports, and data integrity checks, ensuring that stored data remains secure and meets regulatory requirements. The clean, modern design reflects a professional software environment focused on organization, accessibility, and security.

Archiving software provides a systematic approach to long-term data storage, ensuring that essential files remain secure, accessible, and compliant with industry regulations. These platforms reduce storage costs through compression and deduplication while implementing robust search and indexing tools to simplify data retrieval. Additionally, advanced security measures, lifecycle management features, and disaster recovery integration ensure that archived data remains protected and reliable.
Archiving software automates data storage by setting predefined rules for archiving schedules. This reduces manual workload and ensures that important files are stored without human intervention.
By eliminating redundant files and compressing data, archiving solutions significantly reduce storage requirements, making them cost-effective and efficient.
To prevent unauthorized access, archiving software employs strong encryption protocols, such as AES-256, ensuring that data remains confidential.
Organizations must adhere to industry-specific data retention laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. Archiving software helps maintain compliance by enforcing policies on data storage and access.
Whether for a small business or an enterprise with massive data storage needs, archiving software can scale storage capacity dynamically.
Powerful search functionalities enable users to locate archived files quickly. Indexing metadata enhances retrieval speed and accuracy.
Archiving software can handle diverse file types, including documents, emails, multimedia, and structured databases, ensuring broad applicability.
Organizations can choose between cloud-based archiving for remote accessibility or on-premises solutions for tighter security and control.
To prevent corruption and unauthorized modifications, integrity verification mechanisms ensure data consistency and authenticity over time.
Archiving software automates retention schedules, ensuring that outdated files are securely deleted or transitioned to deeper archival storage.
By integrating with backup solutions, archiving software guarantees data redundancy and quick recovery in case of system failure.
Granular permission settings allow administrators to restrict access based on user roles, ensuring that only authorized personnel can retrieve sensitive data.
Backup software creates copies of data for disaster recovery, while archiving software stores data long-term for compliance, reference, and storage optimization.
It ensures data retention policies align with laws such as GDPR and HIPAA, preventing unauthorized modifications and enabling audit trails.
Yes, most solutions support various formats, including images, videos, and audio files, ensuring comprehensive archiving capabilities.
Indexing and metadata tagging enable quick retrieval of archived files, allowing users to find documents based on keywords, dates, or categories.
Cloud archiving offers scalability and remote access, while on-premises solutions provide greater control over security and compliance. The choice depends on organizational needs.
Archiving software uses deduplication algorithms to identify and remove redundant copies of data before storing them. This process involves comparing file hashes or block-level data segments to eliminate duplicate files while retaining only a single instance. Deduplication significantly reduces storage requirements and enhances efficiency, particularly in environments handling large datasets like enterprise document management or email archiving systems.
Metadata is essential for organizing, indexing, and retrieving archived data. When a file is archived, the software generates metadata containing information such as timestamps, file type, author, and access history. This metadata is stored separately or within a database, allowing for advanced search functionality, classification, and automated retention policy enforcement. Structured metadata also enables compliance tracking and facilitates legal discovery processes.
Tiered storage in archiving software categorizes data into different storage classes based on access frequency and retention policies. Frequently accessed data may be stored on high-performance SSDs, while older or less critical files are moved to cost-effective, slower storage solutions such as HDDs, tape libraries, or cloud cold storage. Some solutions use AI-driven automation to migrate data between tiers dynamically, optimizing performance, cost, and accessibility based on real-time usage patterns.