Augmented Reality (AR) software enables users to superimpose digital content onto the real world, blending physical and virtual environments. From entertainment and gaming to industrial design and education, AR software is widely used across industries.
Popular AR tools include Unity AR Foundation, Vuforia, 8th Wall, Lens Studio, and Apple ARKit. These platforms provide developers with the tools to create immersive AR applications.
AR software often overlaps with these software categories: virtual reality (VR) software, 3D modeling tools, and computer vision technologies.

Vuforia – Offers robust object recognition and AR tracking for industrial and enterprise applications.
8th Wall – Web-based AR platform supporting markerless AR for mobile browsers.
Unity AR Foundation – A flexible AR development framework for creating AR apps across multiple platforms.
Apple ARKit – AR development framework for iOS, supporting motion tracking and environmental understanding.
Google ARCore – Google’s AR SDK enabling markerless AR and environmental mapping.
Lens Studio – Snapchat’s AR creation tool for interactive filters and lenses.
Spark AR Studio – Meta’s (Facebook) platform for designing AR experiences on social media.
ZapWorks – A user-friendly AR toolkit for businesses and marketers.
Magic Leap – AR headset software designed for enterprise use in healthcare and manufacturing.
Microsoft HoloLens – Mixed reality platform focused on enterprise and industrial applications.
The Augmented Reality Software Feature Comparison table below highlights key functionalities across three leading AR platforms: Vuforia, 8th Wall, and Unity AR Foundation. These tools vary in object recognition, spatial mapping, and cloud integration capabilities.
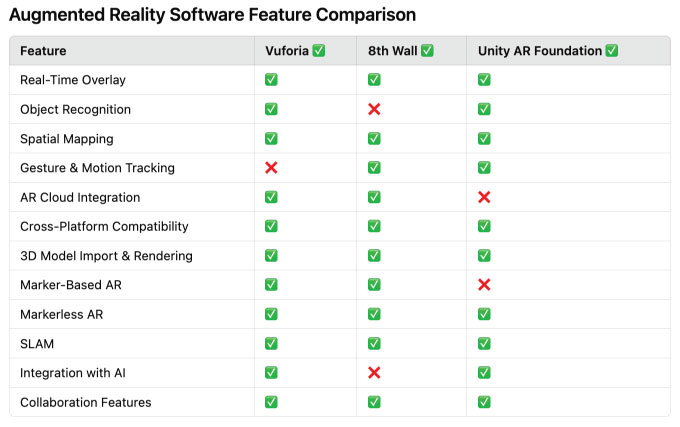
The Augmented Reality Software Feature Comparison table highlights differences among Vuforia, 8th Wall, and Unity AR Foundation. All three support real-time overlay, spatial mapping, and markerless AR, making them versatile AR development tools. Vuforia excels in object recognition and AI integration, while 8th Wall specializes in web-based AR with strong gesture tracking and cloud features. Unity AR Foundation provides broad platform support and powerful 3D rendering but lacks AR cloud integration and marker-based AR support. These distinctions help developers choose the best tool based on their project needs.
Augmented reality (AR) is transforming the way we interact with the world by blending digital content with real environments. In this video, 10 Best Examples of Augmented Reality, you’ll see real-world applications of AR software in action—from immersive gaming and interactive retail experiences to cutting-edge industrial and medical solutions. These examples showcase key AR software features like real-time overlay, object recognition, spatial mapping, and gesture tracking, illustrating how different industries are leveraging AR to enhance user experiences and productivity. Whether you’re a developer, business owner, or just curious about AR technology, this video provides a compelling look at the power of augmented reality in everyday life.
This example dashboard image represents a futuristic augmented reality (AR) software interface, showcasing key tools used in AR development. The dashboard features a 3D model viewer, allowing users to visualize and manipulate digital objects in a real-world context. Spatial mapping tools help developers scan and map physical environments for precise AR object placement. The interface also includes object recognition settings, which enable the software to detect and interact with real-world elements. Real-time overlay adjustments allow for fine-tuning AR effects, ensuring a seamless blend between digital and physical elements. The dark mode UI, enhanced with blue and neon highlights, gives the interface a modern, high-tech aesthetic, reflecting the cutting-edge nature of AR development.
AR software relies on advanced technologies such as computer vision, real-time rendering, and spatial tracking to create seamless digital experiences within real-world settings. Features like object recognition, SLAM, and AI integration enhance realism, while cross-platform support and AR cloud enable scalability.
Real-Time Overlay
AR software enables real-time augmentation of the environment by overlaying digital content, such as 3D models, animations, or information, on live camera feeds. This feature is crucial for interactive experiences in gaming, shopping, and industrial applications.
Object recognition allows AR applications to identify and interact with real-world objects. This is useful in applications like AR instruction manuals, where users can scan a product to receive step-by-step assembly guidance.
Spatial mapping helps AR software understand the dimensions and layout of a physical space. By analyzing depth and surfaces, it ensures that AR objects are positioned realistically, avoiding unnatural floating or misalignment.
AR software detects hand gestures and body movement to allow intuitive control over virtual elements. This is widely used in AR gaming, training simulations, and interactive installations.
The AR cloud stores and synchronizes spatial data, allowing multiple users to experience the same AR content in a shared environment. This is key for collaborative applications like remote teamwork and AR-assisted retail experiences.
AR applications can run on various devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and dedicated AR headsets like the Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap. This ensures broad accessibility.
AR software supports 3D model integration, allowing designers and developers to place realistic objects in real-world environments. This is crucial for architecture, interior design, and product visualization.
Marker-based AR relies on predefined images or QR codes to trigger digital overlays. It is commonly used in marketing campaigns, educational tools, and AR-enhanced packaging.
Unlike marker-based AR, markerless technology allows users to place virtual objects anywhere in their environment without predefined triggers. This is essential for interior design previews and AR navigation systems.
SLAM technology enables AR experiences that do not rely on GPS. Instead, it uses visual and sensor data to track device movement and map surroundings in real time. This is crucial for AR navigation and interactive experiences.
AI-driven AR enhances object recognition, gesture control, and automation. AI-powered AR applications can provide personalized recommendations, improve facial tracking, and enable more natural user interactions.
Multi-user AR experiences allow teams to collaborate in virtual spaces overlaid on the real world. This is useful for remote work, training simulations, and immersive presentations.
AR software is used in gaming, retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and education to overlay digital elements on real-world environments.
AR software runs on smartphones, tablets, AR glasses (e.g., HoloLens, Magic Leap), and VR/AR headsets.
AR enhances real environments with digital elements, while VR creates fully immersive virtual worlds.
Yes, platforms like ZapWorks and Lens Studio offer no-code/low-code AR development tools.
arker-based AR uses predefined images or QR codes to trigger AR content.
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) enables AR to track device movement and map environments without GPS.
Costs vary; some platforms offer free versions, while enterprise solutions can be costly.
AI enhances object recognition, gesture tracking, and interactive AR experiences.
Retail, healthcare, manufacturing, real estate, and education all leverage AR technology.
Common languages include C#, JavaScript, Swift, and Python, depending on the platform.